To stake out a polyline
Polylines are two or more lines or arcs connected together. If required, you can create a polyline from existing points in the map. See To key in a polyline.
Before you start, configure your navigation display settings. You can stake relative to a DTM or the design elevation, if required.
-
To select the polyline:
- From the map, you can:
- Select the polyline and tap Stakeout.
Double‑tap the polyline in the map.
When selecting a polyline to stake out from the map, tap near the end of the polyline that you want to designate as the start. Arrows are then drawn on the polyline to indicate the direction. If the direction is incorrect, tap the polyline to deselect it and then tap it at the correct end to reselect the polyline in the direction required. Alternatively tap and hold in the map and select Reverse polyline direction from the menu.
If the polyline has been offset, the offset directions are not swapped when the polyline direction is reversed.
- From the menu, tap
and select Stakeout / Polylines.
- From the map, you can:
- In the Stake field, select the method and then fill out the required fields. Refer to the Polyline stakeout methods below.
To select the station to stake, key it in, tap the Sta‑ and Sta+ softkeys, or tap
next to the Station fields to select a station from the list.
- To review the polyline definition, tap Details.
- Enter the Antenna height or Target height, the value of the station to be staked out (if any), and any further details, such as horizontal and vertical offsets.
- Tap Start.
-
The Relative to polyline navigation deltas are derived by projecting from your current position perpendicular to the polyline to compute the Go Right/Go Left value, with the Go Forward/Go Backward value computed from that station along the polyline to the target station.
-
When the point is within tolerance, measure the point.
The software returns to the map or, if you selected multiple items to stake out, the software returns to the Stake out items list.
Polyline stakeout methods
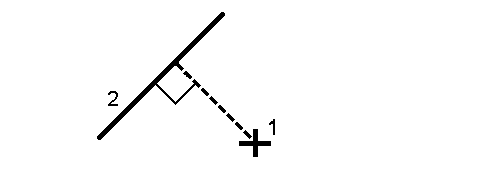
Measure your position (1) relative to a defined polyline (2).
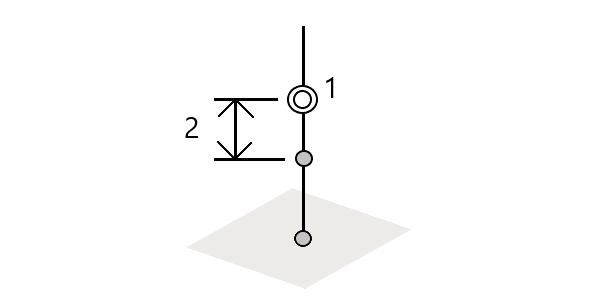
Stake out the distance along a defined polyline (1) at the distance interval (2). The distance and distance interval values are slope distances along the polyline, rather than horizontal distances. This method also enables positions on a vertical polyline to be staked.
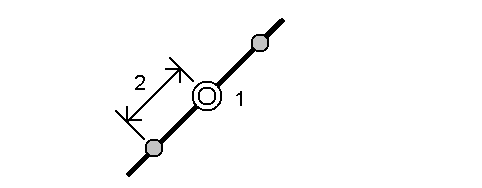
Stake out stations (1) on a defined polyline at the station interval (2) along the polyline.
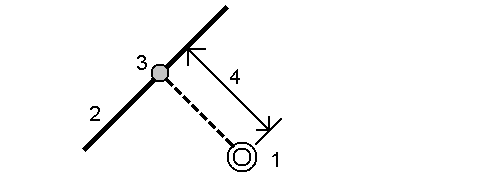
Stake out a point (1) perpendicular to a station (3) on a defined polyline (2) and offset to the left or right by a horizontal distance (4). The design elevation of the point is the same as the elevation of the polyline at the selected station.
You can also apply a vertical offset.
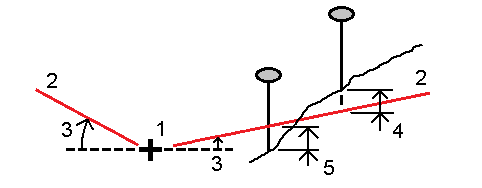
Measure your position relative to a slope (2) defined either side of a defined polyline (1). Each slope can be defined with a different grade (3).
Use the Slope left field and the Slope right field to define the type of grade in one of the following ways:
- horizontal and vertical distance
- grade and slope distance
- grade and horizontal distance
The software reports your position relative to the polyline and the vertical distance as a cut (4) or a fill (5) to the slope.
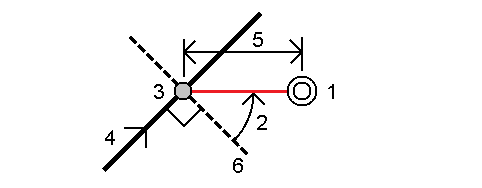
Stake out a point (1) at a skew (2) from a station (3) on a defined polyline (4) and offset to the left or right by a skew distance (5). The skew can be defined by a forward or backward delta angle to a polyline (6) at right angles to the polyline being staked, or the skew can be defined by an azimuth. The diagram shows a point defined by a skew forward and offset to the right.
The elevation for the point can be defined by:
- Slope from polyline – the elevation is computed by a slope from the elevation of the polyline at the entered station
- Delta from polyline – the elevation is computed by a delta from the elevation of the polyline at the entered station.
- Key in – the elevation is keyed in.
If the polyline has no elevation, the elevation for the point must be keyed in.


