DTMs and surfaces
You can view electronic representations of a topograpical surface or digital terrain model (DTM) in the map. The Trimble Access software supports such surfaces in the following file formats:
- gridded terrain models (.dtm)
- triangulated terrain models (.ttm)
- triangular 3D faces in a DXF file (.dxf)
-
triangulated DTMs in a LandXML file (.xml)
You must define a projection and datum transformation before you use a DTM in a GNSS or conventional survey.
To display a DTM in the map, tap in the map toolbar to open the Layer manager and select the Map files tab. Tap the DTM file once to make it visible (
), and tap it again to make points in the file selectable (
). If the file is a DXF or LandXML file, tap the arrow next to the file name and then tap the appropriate layer once to make it visible and again to make it selectable.
When a surface is enabled in the map, a color gradient shows the elevation changes. To disable the color gradient and show only an outline of the surface, tap Options and then clear the Display color gradient check box.
To rotate the surface in the map, tap  and then tap the map and drag to rotate the view. The
and then tap the map and drag to rotate the view. The ![]() icon in the center of the map indicates the point of orbit.
icon in the center of the map indicates the point of orbit.
From the map, you can select points and lines in the surface and then use them in other software functions, for example to perform a Cogo calculation, create a surface, or stakeout.
If you have three or more 3D points in the job, you can create a surface and store it as a triangulated terrain model (TTM) file in the current project folder. You can then use the surface to calculate a volume. See To create a surface.
During a survey, you can use the Measure to surface measurement method to calculate and store the closest distance from the measured point to the selected surface model.
You can stake out points on a DTM or you can stake out points, lines, arcs, or alignments relative to the DTM. See To stake out a DTM and To show the cut/fill to a DTM during stakeout.
You can view the cut and fill relative to the DTM, and specify an offset to raise or lower the DTM. The offset can be applied vertical or perpendicular to the DTM.
- Transfer a DTM file to the appropriate project folder on the controller.
- Make sure the file containing the alignment is visible and selectable in the map.
If it is available, your current position, the DTM elevation, and the distance above (cut) or below (fill) the DTM appear in the map screen.
-
Tap Stakeout.
-
Tap the Options softkey.
- If required, in the Offset to DTM field, specify an offset to the DTM. Tap
and select whether the offset is to be applied vertical or perpendicular to the DTM. The V.Dist DTM value is to the offset position. The offset can be configured in Options when you select the DTM file. When defined, the offset also appears in the Map.
- Tap Accept.
- To change the target or antenna height, tap the target or antenna icon in the status bar.
If the target or antenna height have not been defined, the elevation and cut/fill will be null (?).
When the offset is applied perpendicular to the DTM, the cut/fill value is computed using the following steps:
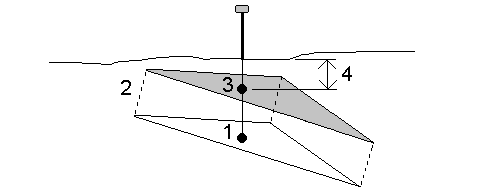
- Determine the triangle that the current position lies on (1).
- Offset that triangle at a right angle by the specified offset value (2) to define a new triangle.
- Compute the elevation of the same position on the new triangle (3).
- Compute the cut/fill value from the computed elevation to the staked position (4).


