Surfaces
A surface can be a topographical or non-topographical:
-
A topographical surface is a digital representation of the shape of a land surface, formed by a mesh of contiguous triangles. The surface may be existing terrain, proposed grade surfaces, or a combination of both.
-
A non-topographical surface is a representation of an object or the face of objects in a 3D model or BIM file.
The Trimble Access software supports topographical surfaces in the following file formats:
- gridded digital terrain models (.dtm)
- triangulated terrain models (.ttm)
- triangular 3D faces in a DXF file (.dxf)
-
triangulated DTMs in a LandXML file (.xml)
-
triangulated DTMs in a 12da file (.12da)
When the offset is applied perpendicular to the DTM, the cut/fill value is computed using the following steps:
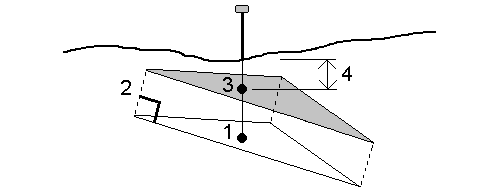
-
Determine the triangle that the current position lies on (1).
-
Offset that triangle at a right angle by the specified offset value (2) to define a new triangle.
-
Compute the elevation of the same position on the new triangle (3).
-
Compute the cut/fill value from the computed elevation to the staked position (4).