Augmented reality viewer
The Augmented reality viewer enables you to interact with your spatial data in the context of the real world. The Augmented reality viewer shows map data in 3D, overlaid on the view from the controller camera. Position and orientation information is provided by the connected GNSS receiver.
The Augmented reality viewer is available only when you are running Trimble Access on a Trimble TSC7, TSC5, or TDC600 controller and you have started a survey using a Trimble GNSS receiver with IMU tilt compensation.
Use the Augmented reality viewer to:
- Visualize map data in 3D, overlaid on the view from the controller camera.
- Use for guidance before beginning precise stakeout.
- Capture images that show the site as well as the features overlaid on the site.
- Document important visual information and share it with stakeholders.
Map backgrounds, including images and Trimble Maps are not shown in the Augmented reality viewer. Job data and supported map files, including BIM models and DXF files, are shown. You can use any map tools, including the Layer manager, Limit box, Snap-to toolbar, and CAD toolbar to work with the any of the data shown in the Augmented reality viewer.
-
In the Rover options page of the RTK survey style, make sure the IMU tilt compensation and the AR viewer check boxes are enabled in the Tilt group.
-
Connect to the GNSS receiver and start the survey.
-
To open the Augmented reality viewer, tap
in the map toolbar. The GNSS antenna settings screen appears.
-
If you have not yet entered the antenna height, in the Measured to field, select where you are measuring the antenna height to and then enter the height value in the Antenna height field.
-
Configure the AR camera setup fields to match how the controller is mounted to the pole. The Trimble Access software uses this information to calculate the position of the controller camera lens relative to the GNSS receiver. For information about mounting options, see AR camera setup options below.
-
Tap Accept.
The Augmented reality viewer appears, showing the camera feed from the controller camera.
-
Make sure the IMU is well‑aligned by walking a short distance (generally less than 3 meters) while changing direction a few times. A well‑aligned IMU will help you to align the camera in the next step.
When the IMU is aligned, the receiver icon in the status bar changes from
 to
to  and the status line shows IMU aligned.
and the status line shows IMU aligned. -
Align the camera feed with the map data.
Once the camera is aligned with the data, you can measure points or select points for stakeout.
-
When staking out, the Stakeout AR icon
 is displayed over the point you are staking out to make it easy to view in the AR mode. The usual stakeout navigation form appears alongside the Augmented reality viewer.
is displayed over the point you are staking out to make it easy to view in the AR mode. The usual stakeout navigation form appears alongside the Augmented reality viewer. -
To save a screen capture that includes the model overlay, press the camera key on the controller keypad or tap
. The current Transparency setting is used for the image. To save a screen capture and then automatically open the Media file screen so that you can annotate the image, long-press the camera key or tap and hold
.
To use a standard AR camera setup, you must use the standard pole mount bracket for your Trimble controller. These are:
-
TSC7: Pole mount and adjustable bracket arm P/N 121349-01-1.
-
TSC5: Quick release pole mount and adjustable bracket arm P/N 121951-01-GEO.
-
TDC600: Pole bracket P/N 117057-GEO-BKT.
If you are not using a standard Trimble pole bracket, use a custom AR camera setup. See Custom AR camera setup below.
-
Attach the controller to the bracket using the 4 outer screw holes. You will be able to fit the bracket to the pole so that the controller is on the right side or the left side of the pole.
-
Fit the bracket to the pole so that you are squarely facing the controller and the LED panel of the receiver.
-
Select Standard in the Setup configuration field.
-
In the Mount field, select whether the controller is mounted on the right hand or left hand side of the pole.
-
In the Clamp height field, enter the height from the pole tip to the top of the pole clamp (1). as indicated in the image below.

-
Fit the bracket to the pole so that you are squarely facing the controller and the LED panel of the receiver.
-
Fit the controller to the pole bracket, oriented to landscape.
-
Select Standard in the Setup configuration field.
-
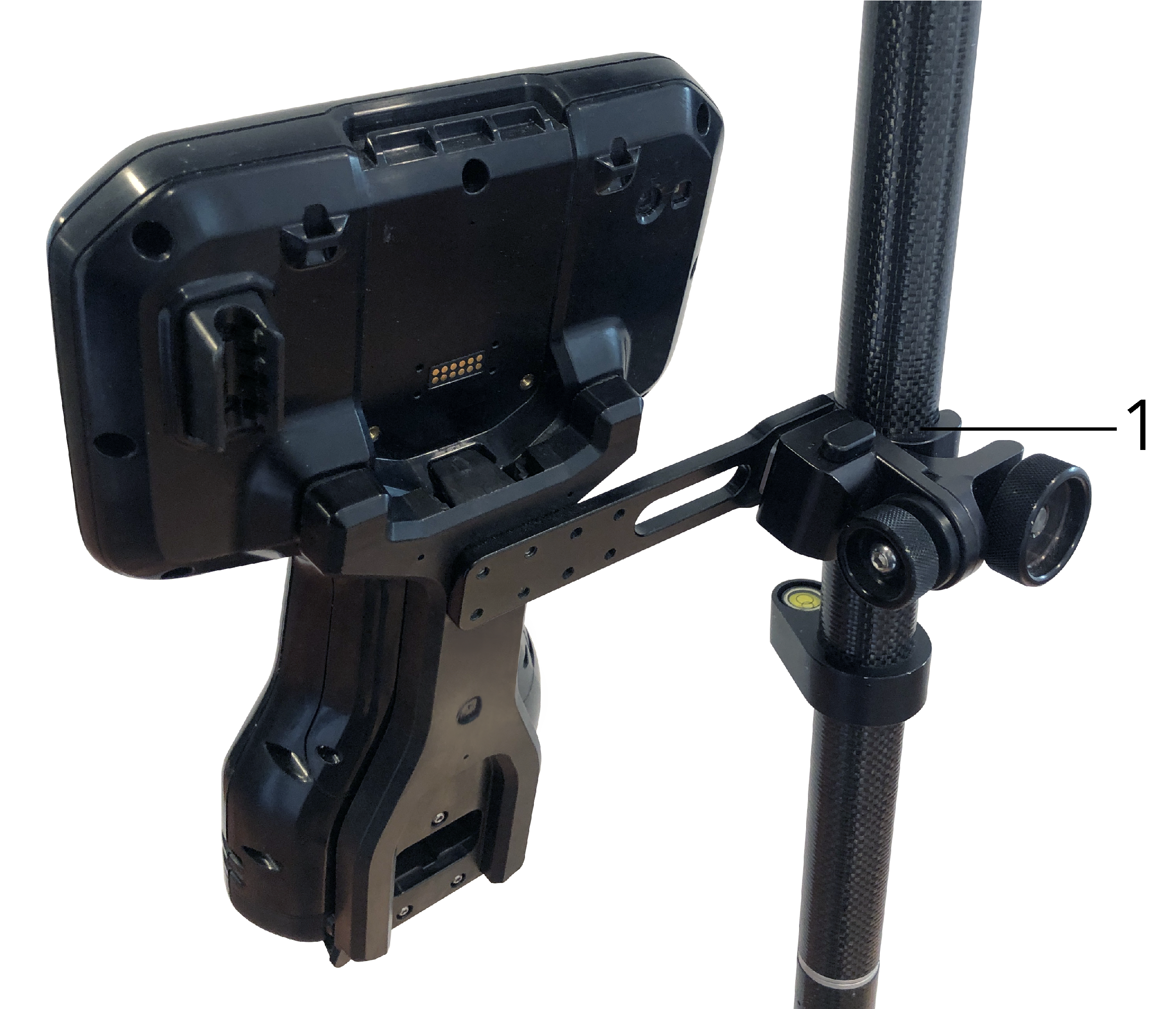
In the Clamp height field, enter the height from the pole tip to the top of the pole clamp (1). as indicated in the image below.

Use a custom AR camera setup only if you are not using a standard Trimble pole bracket.
-
Fit the bracket to the pole so that you are squarely facing the controller and the LED panel of the receiver.
-
Select Custom in the Setup configuration field.
-
In the X field, enter the distance left or right from the center of the pole to the center of the camera lens on the controller.
A positive value indicates the camera lens is to the right of the pole tip, a negative value indicates the camera lens is to the left of the pole tip.
-
In the Y field, enter the distance forward or back from the center of the pole to the center of the camera lens on the controller.
A positive value indicates the camera lens is forward of the center of the pole (that is, away from you). A negative value indicates the camera lens is back from the center of the pole (that is, toward you).
-
In the Z field, enter the height from the pole tip to the center of the camera lens on the controller.
Use the camera alignment controls to align the camera feed with the data shown on screen.
To do this you need to be able to align a virtual element on-screen that aligns with something you can easily identify in the physical world. You can use:
-
A point in the job or in a linked CSV file that can align with a physical point at your location.
-
A BIM model that you can align with the as-built model in the physical world.
-
Virtual markers that you add in the Augmented reality viewer and then align with items that are easy to see in the physical world, for example an access cover or a kerb edge.
Before beginning the camera alignment, make sure the IMU is well‑aligned by walking a short distance (generally less than 3 meters) while changing direction a few times. A well-aligned IMU will help prevent movement while you are aligning the camera. When the IMU is aligned, the receiver icon in the status bar changes from  to
to  and the status line shows IMU aligned.
and the status line shows IMU aligned.
-
To start aligning the camera, tap
in the toolbar. The Camera alignment controls appear.
-
If you need to add virtual markers:
-
Position the pole tip at the location of a physical feature that is easy to see in the camera feed, for example an access cover or a kerb edge. Tap Add marker.
The virtual marker icon
 appears at your location in the Augmented reality viewer. The location of any virtual marker is temporarily saved in the job until the survey ends.
appears at your location in the Augmented reality viewer. The location of any virtual marker is temporarily saved in the job until the survey ends. -
Step back to see the marker displayed in the Augmented reality viewer.
-
Add one or two additional virtual markers as needed. When adding additional virtual markers, position the pole tip at a location that is on the same axis as the previous virtual marker location but at some distance, for example further along the kerb edge.
-
-
Use the sliders in the Camera alignment pop-up to align the physical objects shown in the camera feed with the digital data or virtual markers on‑screen:
-
Use the Pitch slider control to fine-tune the vertical axis (tilt) of the camera. Adjusting the Pitch slider moves the camera view up or down in relation to the data.
-
Use the Yaw slider control to fine-tune the horizontal axis (pan) of the camera. Adjusting the Yaw slider moves the camera view left or right in relation to the data.
If a coarse adjustment is required, make sure the LED panel of the receiver and the controller screen are facing you squarely. If they are not, you can loosen the bracket clamp and rotate the pole slightly and then use the Yaw slider for fine-tuning.
-
Use the Roll slider control to adjust both the horizontal and vertical axes of the camera. Adjusting the Roll slider to moves the camera up or down as well as left or right in relation to the data. In general adjusting the Roll slider is less common than adjusting the Pitch and Yaw sliders.
-
Use the Scale slider control to fine-tune the rendering of the scale used for the model in the Augmented reality viewer. To use the Scale, position a well aligned object near the screen center then adjust the scale to get objects near the screen edges aligned.
To reset the Camera alignment settings to default values, tap the Reset softkey.
-
-
If you remain stationary for too long the IMU will start to drift, making it difficult to align the digital data with objects in the physical world. In that case, realign the IMU.
-
To close the Camera alignment pop-up, tap the X in the corner of the pop-up window.
Once the camera is aligned with the data, you can measure points or select points for stakeout.
Use the Transparency slider control to control the transparency of the camera feed, BIM models and point cloud data in the Augmented reality viewer.
Points, lines, arcs, and polylines and feature labels remain full intensity, regardless of the Transparency slider setting.
The mid point of the Transparency slider enables you to see both the camera feed and the map data at 50% transparency.
-
To make map data more transparent, tap on the left of the slider, or tap and drag the control to the left. At the very left of the slider
, only the camera feed is visible and the map data is 100% transparent.
-
To make the camera feed more transparent, tap on the right of the slider, or tap and drag the control to the right. At the very right of the slider
, only the map data is visible and the camera feed is 100% transparent.